QSPR on Estimating of Polychlorinated Biphenyls Relative Response Factor using Molecular Descriptors Family
Lorentz JÄNTSCHI
Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, Romania, http://lori.academicdirect.org
Abstract
The molecular descriptors family methodology was applied on relative response factor of polychlorinated biphenyls in order to obtain quantitative structure-property relationships.
The use of molecular descriptors family allows making of important remarks about nature of the relative response factor property and its causality.
The obtained quantitative structure-property relationships can explain over 62% of polychlorinated biphenyls relative response factors.
Keywords:
polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), molecular descriptors family (MDF), multiple linear regression (MLR), quantitative structure-property relationship (QSPR)
Introduction
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are a group of 209 synthetic halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons, being a lipophilic group of global pollutants. The PCBs have different toxicity and biological effects including death, birth defects, reproductive failure, liver damage, tumors [[1], [2]]. The compounds were used in the electricity generating industry as insulating and coolant agents in transformers and capacitors [[3], [4]] because they do not burn easily and are good insulators. PCBs were produce commercially since 1929, till 1977 in U.S. but they are still present in environmental samples from the polar regions of air, snow, water, and living organisms [[5]-[7]] being widely pollutants.
A quantitative structure-property relationship (QSPR) relates a quantitative measurable property of chemical, physical, or even biological property and is a technique used today in many domains, including pharmaceutical, environmental, biological domains. Today, the literature contains a lot of QSPR equations for many parameters used to assess the risk of chemicals in the environment [[8]-[11]]. Most of the QSPR equation are based on linear regression analysis [[12]] or by the artificial neural networks [[13]-[16]].
The aim of this paper is to present the ability of the molecular descriptors family (MDF) in estimation of relative response factor of PCBs, using the data from Mullin et al. [[17]] which synthesized and determined the retention times and response factors relative to a reference standard (octachloronaphthalene) of all 209 congeners (Table 1) by using temperature-programmed, high resolution gas chromatography, and electron-capture detection methods (HRGC/ECD).
Material
All 209 PCBs were included into the study. PCBs are synthetic chlorinated hydrocarbon compounds that consist of two benzene rings linked by a single carbon–carbon bond, with from 1 to all 10 of the hydrogen atoms replaced with chlorines. The generic structure of the PCBs is:
PCBs are produced by chlorination of a biphenyl with anhydrous chlorine in the presence of iron filing or ferric chloride as the catalyst being possible ten degree of chlorination and producing 10 PCBs congener group: mono-, di-, tri-, terta-, penta-, hexa-, hepta-, octa-, nona-, decachlorobiphenyl. Table 1 contains the PBCs number, the structure (chlorine-filled) and the measured property (relative response factor, rrf).
Table 1. Polychlorinated biphenyls relative response factors (rrf)
|
PCB |
Chlorines |
rrf |
|
PCB |
Chlorines |
rrf |
|
PCB |
Chlorines |
rrf |
|
1 |
2 |
0.0251 |
|
71 |
2,3',4',6 |
0.468 |
|
141 |
2,2',3,4,5,5' |
1.352 |
|
2 |
3 |
0.0393 |
|
72 |
2,3',5,5' |
0.5515 |
|
142 |
2,2',3,4,5,6 |
1.218 |
|
3 |
4 |
0.04 |
|
73 |
2,3',5',6 |
0.5805 |
|
143 |
2,2',3,4,5,6' |
0.7088 |
|
4 |
2,2' |
0.0374 |
|
74 |
2,4,4',5 |
0.671 |
|
144 |
2,2',3,4,5',6 |
0.8764 |
|
5 |
2,3 |
0.119 |
|
75 |
2,4,4',6 |
0.6461 |
|
145 |
2,2',3,4,6,6' |
0.6789 |
|
6 |
2,3' |
0.38 |
|
76 |
2',3,4,5 |
0.5795 |
|
146 |
2,2',3,4',5,5' |
0.728 |
|
7 |
2,4 |
0.69 |
|
77 |
3,3',4,4' |
0.3812 |
|
147 |
2,2',3,4',5,6 |
0.6 |
|
8 |
2,4' |
0.206 |
|
78 |
3,3',4,5 |
1.1151 |
|
148 |
2,2',3,4',5,6' |
0.554 |
|
9 |
2,5 |
0.388 |
|
79 |
3,3',4,5' |
0.881 |
|
149 |
2,2',3,4',5',6 |
0.572 |
|
10 |
2,6 |
0.262 |
|
80 |
3,3',5,5' |
0.7278 |
|
150 |
2,2',3,4',6,6' |
0.5676 |
|
11 |
3,3' |
0.0449 |
|
81 |
3,4,4',5 |
0.7159 |
|
151 |
2,2',3,5,5',6 |
0.785 |
|
12 |
3,4 |
0.179 |
|
82 |
2,2',3,3',4 |
0.773 |
|
152 |
2,2',3,5,6,6' |
0.5235 |
|
13 |
3,4' |
0.2 |
|
83 |
2,2',3,3',5 |
0.6339 |
|
153 |
2,2',4,4',5,5' |
0.688 |
|
14 |
3,5 |
0.3047 |
|
84 |
2,2',3,3',6 |
0.386 |
|
154 |
2,2',4,4',5,6' |
0.57 |
|
15 |
4,4' |
0.107 |
|
85 |
2,2',3,4,4' |
0.7396 |
|
155 |
2,2',4,4',6,6' |
0.586 |
|
16 |
2,2',3 |
0.447 |
|
86 |
2,2',3,4,5 |
0.7968 |
|
156 |
2,3,3',4,4',5 |
1.389 |
|
17 |
2,2',4 |
0.412 |
|
87 |
2,2',3,4,5' |
1.021 |
|
157 |
2,3,3',4,4',5' |
1.1965 |
|
18 |
2,2',5 |
0.313 |
|
88 |
2,2',3,4,6 |
0.6892 |
|
158 |
2,3,3',4,4',6 |
1.132 |
|
19 |
2,2',6 |
0.3037 |
|
89 |
2,2',3,4,6' |
0.561 |
|
159 |
2,3,3',4,5,5' |
0.9934 |
|
20 |
2,3,3' |
0.7238 |
|
90 |
2,2',3,4',5 |
0.611 |
|
160 |
2,3,3',4,5,6 |
1.1914 |
|
21 |
2,3,4 |
1.0598 |
|
91 |
2,2',3,4',6 |
0.571 |
|
161 |
2,3,3',4,5',6 |
0.9672 |
|
22 |
2,3,4' |
1.0935 |
|
92 |
2,2',3,5,5' |
0.5375 |
|
162 |
2,3,3',4',5,5' |
1.0322 |
|
23 |
2,3,5 |
0.5 |
|
93 |
2,2',3,5,6 |
0.6676 |
|
163 |
2,3,3',4',5,6 |
0.9976 |
|
24 |
2,3,6 |
0.793 |
|
94 |
2,2',3,5,6' |
0.4514 |
|
164 |
2,3,3',4',5',6 |
0.9848 |
|
25 |
2,3',4 |
0.5 |
|
95 |
2,2',3,5',6 |
0.443 |
|
165 |
2,3,3',5,5',6 |
1.0777 |
|
26 |
2,3',5 |
0.603 |
|
96 |
2,2',3,6,6 |
0.4308 |
|
166 |
2,3,4,4',5,6 |
1.0421 |
|
27 |
2,3',6 |
0.495 |
|
97 |
2,2',3',4,5 |
0.631 |
|
167 |
2,3',4,4',5,5' |
1.0658 |
|
28 |
2,4,4' |
0.854 |
|
98 |
2,2',3',4,6 |
0.6246 |
|
168 |
2,3',4,4',5',6 |
0.8375 |
|
29 |
2,4,5 |
0.6339 |
|
99 |
2,2',4,4',5 |
0.613 |
|
169 |
3,3',4,4',5,5' |
0.8355 |
|
30 |
2,4,6 |
0.8202 |
|
100 |
2,2',4,4',6 |
0.5871 |
|
170 |
2,2',3,3',4,4',5 |
0.75 |
|
31 |
2,4',5 |
0.562 |
|
101 |
2,2',4,5,5' |
0.668 |
|
171 |
2,2',3,3',4,4',6 |
1.1712 |
|
32 |
2,4',6 |
0.278 |
|
102 |
2,2',4,5,6' |
0.4561 |
|
172 |
2,2',3,3',4,5,5' |
1.172 |
|
33 |
2',3,4 |
0.447 |
|
103 |
2,2',4,5',6 |
0.6068 |
|
173 |
2,2',3,3',4,5,6 |
2.044 |
|
34 |
2',3,5 |
0.6092 |
|
104 |
2,2',4,6,6 |
0.4561 |
|
174 |
2,2',3,3',4,5,6' |
0.806 |
|
35 |
3,3',4 |
0.3746 |
|
105 |
2,3,3',4,4' |
0.94 |
|
175 |
2,2',3,3',4,5',6 |
0.381 |
|
36 |
3,3',5 |
0.2948 |
|
106 |
2,3,3',4,5 |
1.0046 |
|
176 |
2,2',3,3',4,6,6' |
1.0589 |
|
PCB |
Chlorines |
rrf |
|
PCB |
Chlorines |
rrf |
|
PCB |
Chlorines |
rrf |
|
37 |
3,4,4' |
0.58 |
|
107 |
2,3,3',4',5 |
0.8183 |
|
177 |
2,2',3,3',4',5,6 |
1.0009 |
|
38 |
3,4,5 |
0.722 |
|
108 |
2,3,3',4,5' |
1.0654 |
|
178 |
2,2',3,3',5,5',6 |
0.621 |
|
39 |
3,4',5 |
0.347 |
|
109 |
2,3,3',4,6 |
0.9625 |
|
179 |
2,2',3,3',5,6,6' |
0.8237 |
|
40 |
2,2',3,3' |
0.722 |
|
110 |
2,3,3',4',6 |
0.65 |
|
180 |
2,2',3,4,4',5,5' |
1.295 |
|
41 |
2,2',3,4 |
0.5469 |
|
111 |
2,3,3',5,5' |
0.6601 |
|
181 |
2,2',3,4,4',5,6 |
1.6046 |
|
42 |
2,2',3,4' |
0.792 |
|
112 |
2,3,3',5,6 |
0.8286 |
|
182 |
2,2',3,4,4',5,6' |
1.1272 |
|
43 |
2,2',3,5 |
0.503 |
|
113 |
2,3,3',5',6 |
0.604 |
|
183 |
2,2',3,4,4',5',6 |
0.976 |
|
44 |
2,2',3,5' |
0.524 |
|
114 |
2,3,4,4',5 |
1.0261 |
|
184 |
2,2',3,4,4',6,6' |
1.0046 |
|
45 |
2,2',3,6 |
0.54 |
|
115 |
2,3,4,4',6 |
1.1328 |
|
185 |
2,2',3,4,5,5',6 |
1.437 |
|
46 |
2,2',3,6' |
0.468 |
|
116 |
2,3,4,5,6 |
1.3987 |
|
186 |
2,2',3,4,5,6,6' |
1.2236 |
|
47 |
2,2',4,4' |
0.848 |
|
117 |
2,3,4',5,6 |
0.8895 |
|
187 |
2,2',3,4',5,5',6 |
1.122 |
|
48 |
2,2'4,5 |
0.556 |
|
118 |
2,3',4,4',5 |
0.87 |
|
188 |
2,2',3,4',5,6,6' |
0.7337 |
|
49 |
2,2',4,5' |
0.648 |
|
119 |
2,3',4,4',6 |
0.8239 |
|
189 |
2,3,3',4,4',5,5' |
1.5091 |
|
50 |
2,2',4,6 |
0.6817 |
|
120 |
2,3',4,5,5' |
0.7444 |
|
190 |
2,3,3',4,4',5,6 |
1.31 |
|
51 |
2,2',4,6' |
0.6 |
|
121 |
2,3',4,5',6 |
0.7659 |
|
191 |
2,3,3',4,4',5',6 |
1.4741 |
|
52 |
2,2',5,5' |
0.418 |
|
122 |
2',3,3',4,5 |
0.7247 |
|
192 |
2,3,3',4,5,5',6 |
1.599 |
|
53 |
2,2',5,6' |
0.3606 |
|
123 |
2',3,4,4',5 |
0.6645 |
|
193 |
2,3,3',4',5,5',6 |
1.4167 |
|
54 |
2,2',6,6' |
0.3643 |
|
124 |
2',3,4,5,5' |
0.848 |
|
194 |
2,2',3,3',4,4',5,5' |
1.868 |
|
55 |
2,3,3',4 |
0.829 |
|
125 |
2',3,4,5,6' |
0.556 |
|
195 |
2,2',3,3',4,4',5,6 |
0.415 |
|
56 |
2,3,3',4' |
0.829 |
|
126 |
3,3',4,4'5 |
0.4757 |
|
196 |
2,2',3,3',4,4',5',6 |
1.2321 |
|
57 |
2,3,3',5 |
0.6 |
|
127 |
3,3',4,5,5' |
0.5834 |
|
197 |
2,2',3,3',4,4',6,6' |
0.9522 |
|
58 |
2,3,3',5' |
0.609 |
|
128 |
2,2',3,3',4,4' |
1.188 |
|
198 |
2,2',3,3',4,5,5',6 |
1.07 |
|
59 |
2,3,3',6 |
0.6 |
|
129 |
2,2',3,3',4,5 |
0.997 |
|
199 |
2,2',3,3',4,5,6,6' |
1.1508 |
|
60 |
2,3,4,4' |
1.0164 |
|
130 |
2,2',3,3',4,5' |
0.952 |
|
200 |
2,2',3,3',4,5',6,6' |
0.369 |
|
61 |
2,3,4,5 |
1.2227 |
|
131 |
2,2',3,3',4,6 |
0.8492 |
|
201 |
2,2',3,3',4',5,5',6 |
0.803 |
|
62 |
2,3,4,6 |
1.1478 |
|
132 |
2,2',3,3',4,6' |
0.7303 |
|
202 |
2,2',3,3',5,5',6,6' |
1.165 |
|
63 |
2,3,4',5 |
0.728 |
|
133 |
2,2',3,3',5,5' |
1.148 |
|
203 |
2,2',3,4,4',5,5',6 |
1.629 |
|
64 |
2,3,4',6 |
0.607 |
|
134 |
2,2',3,3',5,6 |
0.7331 |
|
204 |
2,2',3,4,4',5,6,6' |
0.8034 |
|
65 |
2,3,5,6 |
0.8408 |
|
135 |
2,2',3,3',5,6' |
0.7031 |
|
205 |
2,3,3',4,4',5,5',6 |
1.406 |
|
66 |
2,3',4,4' |
0.646 |
|
136 |
2,2',3,3',6,6' |
0.444 |
|
206 |
2,2',3,3',4,4',5,5',6 |
1.673 |
|
67 |
2,3',4,5 |
0.6 |
|
137 |
2,2',3,4,4',5 |
1.112 |
|
207 |
2,2',3,3',4,4',5,6,6' |
1.3257 |
|
68 |
2,3',4,5' |
0.726 |
|
138 |
2,2',3,4,4',5' |
0.827 |
|
208 |
2,2',3,3',4,5,5',6,6' |
1.1756 |
|
69 |
2,3',4,6 |
0.8024 |
|
139 |
2,2',3,4,4',6 |
0.7219 |
|
209 |
2,2',3,3',4,4',5,5',6,6' |
1.139 |
|
70 |
2,3',4',5 |
0.658 |
|
140 |
2,2',3,4,4',6' |
0.6732 |
|
|
|
|
Methods
Opposing to the Wiener [[18]-[21]], Randic [[22]], molecular connectivity [[23]] which consider strictly the topological structure of the molecule as the only structure descriptor, the MDF considers both topological structure and topographical shape of the molecule as essential contributors to the molecular property behavior.
The MDF methodology starts with 3D structure of molecules constructing using a molecular modeling program (such as HyperChem), partial charge distribution calculations (using a method like semi-empirical Extended Hückel Single Point Approach) and calculation of a huge number (787968) of molecular descriptors based on different assumptions [[24]].
The MDF methodology continues with cleaning of the family by the undefined, trivial and identical values members. For the rrf property of PCBs set a number of 98434 members remain in the MDF.
The measured property and the remained MDF members are stored into a database. A set of client-server programs runs for QSPR findings using a MLR (multiple linear regressions) algorithm.
First are found the member which correlates the best with the measured property. Pairs of members enter into bi-varied findings of QSPRs in the second. Multi-varied findings of QSPRs use heuristic algorithms in place of all possible combinations because all possible combinations are almost impossible to be exhausted in real time.
Finally, a query program search for the best obtained results into the results table from the database, and produce a report.
Results
The procedure of QSPRs findings has runs for mono-, bi- and four-varied models. The best mono-varied MDF QSPR, best bi-varied MDF QSPR, and best found four-varied MDF QSPR are gave and discussed.
The calculated values of the members which appear in the QSPRs of PCBs are in table 2.
Table 2. The molecular descriptors used in the QSPR for polychlorinated biphenyls
|
PCB |
iHMdTHg |
10-2imMrFHt |
iHDdFHg |
10-2imMrFHt |
102iMMMjQg |
10-1iAMrVQg |
|
001 |
1.266 |
2.031 |
1.070 |
2.031 |
0.470 |
-0.945 |
|
002 |
1.341 |
2.102 |
1.114 |
2.102 |
2.878 |
-2.070 |
|
003 |
1.277 |
2.102 |
1.126 |
2.102 |
1.490 |
-2.119 |
|
004 |
1.213 |
2.102 |
1.219 |
2.102 |
3.409 |
-1.007 |
|
005 |
1.651 |
2.102 |
1.333 |
2.102 |
1.010 |
-1.291 |
|
006 |
1.586 |
2.102 |
1.281 |
2.102 |
0.657 |
-1.259 |
|
007 |
1.614 |
2.102 |
1.324 |
2.102 |
0.638 |
-1.276 |
|
008 |
1.520 |
2.102 |
1.293 |
2.102 |
1.231 |
-1.360 |
|
009 |
1.581 |
2.102 |
1.282 |
2.102 |
0.684 |
-1.325 |
|
010 |
1.516 |
2.102 |
1.230 |
2.102 |
0.747 |
-0.822 |
|
011 |
1.649 |
2.176 |
1.327 |
2.176 |
2.527 |
-2.985 |
|
012 |
1.698 |
2.176 |
1.388 |
2.176 |
0.613 |
-3.099 |
|
013 |
1.589 |
2.176 |
1.342 |
2.176 |
1.957 |
-3.071 |
|
014 |
1.762 |
2.176 |
1.359 |
2.176 |
2.648 |
-2.891 |
|
015 |
1.529 |
2.176 |
1.356 |
2.176 |
1.327 |
-3.171 |
|
016 |
1.545 |
2.176 |
1.442 |
2.176 |
4.344 |
-1.337 |
|
017 |
1.530 |
2.176 |
1.437 |
2.176 |
4.330 |
-1.178 |
|
018 |
1.538 |
2.176 |
1.408 |
2.176 |
4.759 |
-1.356 |
|
019 |
1.487 |
2.176 |
1.384 |
2.176 |
5.485 |
-1.769 |
|
020 |
1.923 |
2.176 |
1.508 |
2.176 |
1.321 |
-1.676 |
|
021 |
2.069 |
2.176 |
1.607 |
2.176 |
0.966 |
-1.722 |
|
022 |
1.859 |
2.176 |
1.523 |
2.176 |
1.299 |
-1.823 |
|
023 |
2.087 |
2.176 |
1.566 |
2.176 |
1.771 |
-1.704 |
|
024 |
1.960 |
2.176 |
1.527 |
2.176 |
1.821 |
-0.884 |
|
025 |
1.885 |
2.176 |
1.504 |
2.176 |
1.023 |
-1.649 |
|
026 |
1.891 |
2.176 |
1.469 |
2.176 |
1.344 |
-1.676 |
|
027 |
1.844 |
2.176 |
1.455 |
2.176 |
1.827 |
-0.872 |
|
028 |
1.823 |
2.176 |
1.518 |
2.176 |
1.130 |
-1.788 |
|
029 |
2.057 |
2.176 |
1.573 |
2.176 |
0.966 |
-1.702 |
|
030 |
1.996 |
2.176 |
1.526 |
2.176 |
2.667 |
-0.871 |
|
031 |
1.829 |
2.176 |
1.487 |
2.176 |
1.313 |
-1.804 |
|
032 |
1.781 |
2.176 |
1.467 |
2.176 |
2.167 |
-0.922 |
|
033 |
1.901 |
2.176 |
1.515 |
2.176 |
1.316 |
-1.797 |
|
034 |
1.962 |
2.176 |
1.491 |
2.176 |
1.318 |
-1.694 |
|
035 |
1.957 |
2.250 |
1.567 |
2.250 |
4.231 |
-4.251 |
|
036 |
2.018 |
2.250 |
1.535 |
2.250 |
4.223 |
-3.969 |
|
037 |
1.901 |
2.250 |
1.583 |
2.250 |
2.737 |
-4.430 |
|
038 |
2.196 |
2.250 |
1.662 |
2.250 |
2.557 |
-4.211 |
|
039 |
1.961 |
2.250 |
1.555 |
2.250 |
3.848 |
-4.060 |
|
040 |
1.832 |
2.250 |
1.636 |
2.250 |
5.775 |
-1.478 |
|
041 |
1.936 |
2.250 |
1.683 |
2.250 |
5.440 |
-2.279 |
|
042 |
1.818 |
2.250 |
1.635 |
2.250 |
5.459 |
-1.603 |
|
043 |
1.954 |
2.250 |
1.648 |
2.250 |
5.503 |
-0.530 |
|
044 |
1.826 |
2.250 |
1.603 |
2.250 |
5.612 |
-1.468 |
|
045 |
1.827 |
2.250 |
1.600 |
2.250 |
6.229 |
-0.745 |
|
046 |
1.778 |
2.250 |
1.577 |
2.250 |
6.301 |
-1.173 |
|
047 |
1.804 |
2.250 |
1.633 |
2.250 |
5.598 |
-1.378 |
|
048 |
1.945 |
2.250 |
1.655 |
2.250 |
4.751 |
-2.459 |
|
049 |
1.812 |
2.250 |
1.606 |
2.250 |
5.040 |
-1.689 |
|
050 |
1.882 |
2.250 |
1.601 |
2.250 |
6.338 |
1.158 |
|
051 |
1.763 |
2.250 |
1.573 |
2.250 |
6.405 |
1.058 |
|
052 |
1.818 |
2.250 |
1.577 |
2.250 |
5.197 |
-1.411 |
|
053 |
1.776 |
2.250 |
1.547 |
2.250 |
0.202 |
-1.160 |
|
054 |
1.436 |
2.250 |
1.499 |
2.250 |
9.935 |
-0.246 |
|
055 |
2.296 |
2.250 |
1.756 |
2.250 |
1.040 |
-2.184 |
|
056 |
2.196 |
2.250 |
1.714 |
2.250 |
1.101 |
-2.369 |
|
057 |
2.312 |
2.250 |
1.714 |
2.250 |
1.465 |
-2.177 |
|
058 |
2.253 |
2.250 |
1.686 |
2.250 |
1.095 |
-2.218 |
|
059 |
2.190 |
2.250 |
1.678 |
2.250 |
2.054 |
-1.100 |
|
060 |
2.296 |
2.250 |
1.756 |
2.250 |
1.019 |
-2.184 |
|
061 |
2.615 |
2.250 |
1.891 |
2.250 |
0.787 |
-2.251 |
|
062 |
2.492 |
2.250 |
1.817 |
2.250 |
2.827 |
-1.113 |
|
063 |
2.252 |
2.250 |
1.734 |
2.250 |
1.224 |
-2.358 |
|
064 |
2.130 |
2.250 |
1.692 |
2.250 |
2.260 |
-1.168 |
|
065 |
2.467 |
2.250 |
1.803 |
2.250 |
1.886 |
-1.123 |
|
066 |
2.159 |
2.250 |
1.713 |
2.250 |
1.015 |
-2.314 |
|
067 |
2.282 |
2.250 |
1.722 |
2.250 |
1.078 |
-2.170 |
|
068 |
2.216 |
2.250 |
1.689 |
2.250 |
1.151 |
-2.158 |
|
069 |
2.223 |
2.250 |
1.679 |
2.250 |
3.409 |
-1.082 |
|
070 |
2.165 |
2.250 |
1.680 |
2.250 |
1.101 |
-2.354 |
|
071 |
2.120 |
2.250 |
1.658 |
2.250 |
1.943 |
-1.161 |
|
072 |
2.221 |
2.250 |
1.655 |
2.250 |
1.155 |
-2.199 |
|
073 |
2.182 |
2.250 |
1.635 |
2.250 |
2.078 |
-1.081 |
|
074 |
2.222 |
2.250 |
1.742 |
2.250 |
0.993 |
-2.351 |
|
075 |
2.163 |
2.250 |
1.694 |
2.250 |
4.313 |
-1.146 |
|
076 |
2.358 |
2.250 |
1.757 |
2.250 |
1.104 |
-2.411 |
|
077 |
2.225 |
2.326 |
1.777 |
2.326 |
1.842 |
-5.733 |
|
078 |
2.406 |
2.326 |
1.806 |
2.326 |
2.794 |
-5.413 |
|
079 |
2.281 |
2.326 |
1.746 |
2.326 |
2.336 |
-5.259 |
|
080 |
2.337 |
2.326 |
1.714 |
2.326 |
4.508 |
-4.883 |
|
081 |
2.353 |
2.326 |
1.827 |
2.326 |
2.129 |
-5.627 |
|
082 |
2.182 |
2.326 |
1.855 |
2.326 |
6.661 |
-1.884 |
|
083 |
2.199 |
2.326 |
1.818 |
2.326 |
5.951 |
-1.198 |
|
084 |
2.078 |
2.326 |
1.774 |
2.326 |
7.377 |
-1.196 |
|
085 |
2.169 |
2.326 |
1.858 |
2.326 |
6.634 |
5.400 |
|
086 |
2.457 |
2.326 |
1.939 |
2.326 |
5.637 |
-2.306 |
|
087 |
2.176 |
2.326 |
1.826 |
2.326 |
6.510 |
-1.794 |
|
088 |
2.332 |
2.326 |
1.861 |
2.326 |
7.219 |
-1.179 |
|
089 |
2.132 |
2.326 |
1.793 |
2.326 |
8.010 |
-1.368 |
|
090 |
2.185 |
2.326 |
1.825 |
2.326 |
5.760 |
-1.207 |
|
091 |
2.064 |
2.326 |
1.775 |
2.326 |
7.017 |
-1.245 |
|
092 |
2.191 |
2.326 |
1.793 |
2.326 |
5.862 |
-0.302 |
|
093 |
2.309 |
2.326 |
1.851 |
2.326 |
6.592 |
-1.250 |
|
094 |
2.153 |
2.326 |
1.762 |
2.326 |
3.889 |
-1.396 |
|
095 |
2.076 |
2.326 |
1.744 |
2.326 |
9.502 |
-1.268 |
|
096 |
1.750 |
2.326 |
1.694 |
2.326 |
8.815 |
-0.319 |
|
097 |
2.191 |
2.326 |
1.827 |
2.326 |
6.693 |
-3.060 |
|
098 |
2.131 |
2.326 |
1.778 |
2.326 |
7.552 |
-1.373 |
|
099 |
2.177 |
2.326 |
1.833 |
2.326 |
5.638 |
2.140 |
|
100 |
2.117 |
2.326 |
1.778 |
2.326 |
8.989 |
-1.237 |
|
101 |
2.183 |
2.326 |
1.806 |
2.326 |
6.258 |
-1.746 |
|
102 |
2.146 |
2.326 |
1.767 |
2.326 |
0.517 |
-1.397 |
|
103 |
2.129 |
2.326 |
1.751 |
2.326 |
1.224 |
-1.304 |
|
104 |
1.800 |
2.326 |
1.695 |
2.326 |
8.758 |
-0.320 |
|
105 |
2.530 |
2.326 |
1.940 |
2.326 |
1.000 |
-3.045 |
|
106 |
2.798 |
2.326 |
2.013 |
2.326 |
0.918 |
-2.816 |
|
107 |
2.545 |
2.326 |
1.900 |
2.326 |
1.281 |
-3.025 |
|
108 |
2.584 |
2.326 |
1.911 |
2.326 |
1.180 |
-2.816 |
|
109 |
2.678 |
2.326 |
1.948 |
2.326 |
3.845 |
-1.358 |
|
110 |
2.429 |
2.326 |
1.861 |
2.326 |
2.341 |
-1.450 |
|
111 |
2.598 |
2.326 |
1.871 |
2.326 |
1.342 |
-2.809 |
|
112 |
2.654 |
2.326 |
1.929 |
2.326 |
2.199 |
-1.380 |
|
113 |
2.488 |
2.326 |
1.834 |
2.326 |
2.596 |
-1.349 |
|
114 |
2.739 |
2.326 |
2.035 |
2.326 |
0.844 |
-3.075 |
|
115 |
2.619 |
2.326 |
1.965 |
2.326 |
4.850 |
-1.445 |
|
116 |
3.131 |
2.326 |
2.162 |
2.326 |
3.012 |
-1.406 |
|
117 |
2.596 |
2.326 |
1.951 |
2.326 |
2.513 |
-1.462 |
|
118 |
2.515 |
2.326 |
1.910 |
2.326 |
1.003 |
-3.009 |
|
119 |
2.459 |
2.326 |
1.865 |
2.326 |
4.215 |
-1.417 |
|
120 |
2.568 |
2.326 |
1.885 |
2.326 |
1.163 |
-2.778 |
|
121 |
2.518 |
2.326 |
1.842 |
2.326 |
4.395 |
-1.315 |
|
122 |
2.609 |
2.326 |
1.925 |
2.326 |
1.221 |
-3.139 |
|
123 |
2.573 |
2.326 |
1.932 |
2.326 |
1.612 |
-3.035 |
|
124 |
2.578 |
2.326 |
1.898 |
2.326 |
1.284 |
-3.099 |
|
125 |
2.544 |
2.326 |
1.871 |
2.326 |
2.849 |
-1.436 |
|
126 |
2.631 |
2.402 |
1.991 |
2.402 |
1.984 |
-6.649 |
|
127 |
2.684 |
2.402 |
1.959 |
2.402 |
2.489 |
-6.090 |
|
128 |
2.493 |
2.402 |
2.059 |
2.402 |
11.594 |
-2.445 |
|
129 |
2.662 |
2.402 |
2.088 |
2.402 |
9.267 |
-3.022 |
|
130 |
2.509 |
2.402 |
2.023 |
2.402 |
6.822 |
-4.135 |
|
131 |
2.541 |
2.402 |
2.018 |
2.402 |
12.395 |
0.694 |
|
132 |
2.394 |
2.402 |
1.975 |
2.402 |
10.893 |
-1.278 |
|
133 |
2.523 |
2.402 |
1.987 |
2.402 |
8.845 |
-3.576 |
|
134 |
2.520 |
2.402 |
2.003 |
2.402 |
11.802 |
-1.441 |
|
135 |
2.414 |
2.402 |
1.941 |
2.402 |
3.496 |
-3.441 |
|
136 |
2.025 |
2.402 |
1.875 |
2.402 |
7.833 |
-0.414 |
|
137 |
2.501 |
2.402 |
2.033 |
2.402 |
10.196 |
-2.647 |
|
138 |
2.501 |
2.402 |
2.033 |
2.402 |
10.196 |
-2.647 |
|
139 |
2.527 |
2.402 |
2.023 |
2.402 |
10.581 |
-1.938 |
|
140 |
2.445 |
2.402 |
1.981 |
2.402 |
15.550 |
-1.603 |
|
141 |
2.655 |
2.402 |
2.066 |
2.402 |
7.948 |
1.184 |
|
142 |
2.948 |
2.402 |
2.179 |
2.402 |
9.178 |
-4.242 |
|
143 |
2.623 |
2.402 |
2.027 |
2.402 |
4.458 |
-2.230 |
|
144 |
2.540 |
2.402 |
1.991 |
2.402 |
14.219 |
5.992 |
|
145 |
2.225 |
2.402 |
1.932 |
2.402 |
7.675 |
-0.415 |
|
146 |
2.515 |
2.402 |
2.001 |
2.402 |
7.862 |
-1.134 |
|
147 |
2.506 |
2.402 |
2.012 |
2.402 |
8.972 |
-1.447 |
|
148 |
2.465 |
2.402 |
1.951 |
2.402 |
4.526 |
-1.590 |
|
149 |
2.408 |
2.402 |
1.948 |
2.402 |
11.778 |
-1.224 |
|
150 |
2.075 |
2.402 |
1.879 |
2.402 |
7.892 |
-0.416 |
|
151 |
2.519 |
2.402 |
1.980 |
2.402 |
4.014 |
-1.375 |
|
152 |
2.182 |
2.402 |
1.922 |
2.402 |
7.736 |
-0.417 |
|
153 |
2.507 |
2.402 |
2.016 |
2.402 |
8.379 |
-2.257 |
|
154 |
2.457 |
2.402 |
1.958 |
2.402 |
2.261 |
-1.497 |
|
155 |
2.123 |
2.402 |
1.883 |
2.402 |
7.854 |
-0.416 |
|
156 |
2.991 |
2.402 |
2.178 |
2.402 |
0.710 |
-3.863 |
|
157 |
2.903 |
2.402 |
2.130 |
2.402 |
0.865 |
-3.936 |
|
158 |
2.876 |
2.402 |
2.115 |
2.402 |
3.756 |
-1.770 |
|
159 |
3.042 |
2.402 |
2.148 |
2.402 |
0.833 |
-3.541 |
|
160 |
3.274 |
2.402 |
2.267 |
2.402 |
3.502 |
-1.700 |
|
161 |
2.933 |
2.402 |
2.086 |
2.402 |
4.053 |
-1.637 |
|
162 |
2.916 |
2.402 |
2.092 |
2.402 |
0.981 |
-3.914 |
|
163 |
2.854 |
2.402 |
2.096 |
2.402 |
1.827 |
-1.802 |
|
164 |
2.814 |
2.402 |
2.051 |
2.402 |
1.991 |
-1.782 |
|
165 |
2.911 |
2.402 |
2.067 |
2.402 |
2.183 |
-1.666 |
|
166 |
3.218 |
2.402 |
2.293 |
2.402 |
5.007 |
-1.809 |
|
167 |
2.887 |
2.402 |
2.107 |
2.402 |
0.988 |
-3.871 |
|
168 |
2.841 |
2.402 |
2.061 |
2.402 |
4.121 |
-1.728 |
|
169 |
2.993 |
2.481 |
2.180 |
2.481 |
2.031 |
-6.909 |
|
170 |
2.933 |
2.481 |
2.276 |
2.481 |
2.310 |
0.139 |
|
171 |
2.817 |
2.481 |
2.208 |
2.481 |
19.874 |
-1.436 |
|
172 |
2.946 |
2.481 |
2.241 |
2.481 |
15.518 |
-5.458 |
|
173 |
3.117 |
2.481 |
2.314 |
2.481 |
16.680 |
-5.029 |
|
174 |
2.847 |
2.481 |
2.191 |
2.481 |
2.429 |
-0.753 |
|
175 |
2.837 |
2.481 |
2.174 |
2.481 |
2.072 |
-2.424 |
|
176 |
2.461 |
2.481 |
2.102 |
2.481 |
7.217 |
-0.548 |
|
177 |
2.797 |
2.481 |
2.192 |
2.481 |
4.905 |
-1.999 |
|
178 |
2.817 |
2.481 |
2.158 |
2.481 |
6.772 |
-1.425 |
|
179 |
2.419 |
2.481 |
2.087 |
2.481 |
7.229 |
-0.555 |
|
180 |
2.939 |
2.481 |
2.257 |
2.481 |
12.841 |
-1.478 |
|
181 |
3.103 |
2.481 |
2.327 |
2.481 |
14.476 |
5.585 |
|
182 |
2.895 |
2.481 |
2.203 |
2.481 |
5.638 |
-1.707 |
|
183 |
2.830 |
2.481 |
2.183 |
2.481 |
7.556 |
-1.300 |
|
184 |
2.508 |
2.481 |
2.109 |
2.481 |
7.160 |
-0.550 |
|
185 |
3.116 |
2.481 |
2.294 |
2.481 |
0.402 |
-3.275 |
|
186 |
2.794 |
2.481 |
2.224 |
2.481 |
7.032 |
-0.568 |
|
187 |
2.811 |
2.481 |
2.172 |
2.481 |
2.801 |
-1.857 |
|
188 |
2.466 |
2.481 |
2.098 |
2.481 |
7.158 |
-0.557 |
|
189 |
3.322 |
2.481 |
2.349 |
2.481 |
0.936 |
-4.856 |
|
190 |
3.434 |
2.481 |
2.419 |
2.481 |
5.219 |
-2.203 |
|
191 |
3.220 |
2.481 |
2.288 |
2.481 |
4.672 |
-2.148 |
|
192 |
3.489 |
2.481 |
2.388 |
2.481 |
5.306 |
-2.023 |
|
193 |
3.199 |
2.481 |
2.269 |
2.481 |
2.275 |
-2.192 |
|
194 |
3.331 |
2.560 |
2.478 |
2.560 |
13.923 |
-9.996 |
|
195 |
3.354 |
2.560 |
2.491 |
2.560 |
1.815 |
6.194 |
|
196 |
3.229 |
2.560 |
2.411 |
2.560 |
1.215 |
-2.458 |
|
197 |
2.854 |
2.560 |
2.322 |
2.560 |
6.491 |
-0.764 |
|
198 |
3.373 |
2.560 |
2.456 |
2.560 |
4.469 |
-1.637 |
|
199 |
2.992 |
2.560 |
2.378 |
2.560 |
6.451 |
-0.814 |
|
200 |
2.814 |
2.560 |
2.305 |
2.560 |
6.510 |
-0.789 |
|
201 |
3.373 |
2.560 |
2.456 |
2.560 |
4.605 |
-1.637 |
|
202 |
2.773 |
2.560 |
2.289 |
2.560 |
6.470 |
-0.803 |
|
203 |
3.366 |
2.560 |
2.473 |
2.560 |
6.067 |
-12.649 |
|
204 |
3.036 |
2.560 |
2.392 |
2.560 |
6.364 |
-0.821 |
|
205 |
3.738 |
2.560 |
2.574 |
2.560 |
4.708 |
-2.650 |
|
206 |
3.725 |
2.641 |
2.680 |
2.641 |
2.158 |
-2.966 |
|
207 |
3.343 |
2.641 |
2.587 |
2.641 |
5.759 |
-1.455 |
|
208 |
3.304 |
2.641 |
2.569 |
2.641 |
5.849 |
-1.534 |
|
209 |
3.790 |
2.722 |
2.841 |
2.722 |
5.372 |
13.418 |
The best mono-varied MDF QSPR has the equation:
· Ŷ = -5.063·10-1+5.348·10-1·iHMdTHg (1)
where Ŷ is the predicted rrf (Y is the measured rrf), and the iHMdTHg is the member used in estimation and the associated statistical results are:
· r = 0.793 (correlation coefficient); r2 = 0.629 (squared correlation coefficient); s = 0.319 (standard deviation); F = 351 (Fisher estimator); p = 2.01·10-46, (significance of regression model); r2cv = 0.619 (the leave one out square cross validation score). (2)
The graphical representation of the mono-varied MDF QSPR given by the equation (1) is in figure 2.
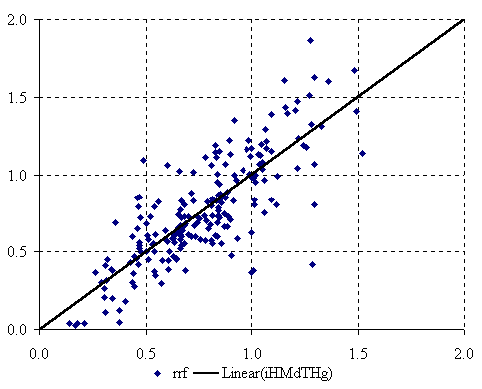
Figure 2. The plot of best mono-varied MDF QSPR
The best bi-varied MDF QSPR is:
· Ŷ = 5.085-357.29·imMrFHt+2.1561·iHDdFHg (3)
and the associated statistical results are:
· r = 0.832; r2 = 0.693; s = 0.1964; F = 232, p = 1.556·10-53; r2(rrf, imMrFHt) = 0.448; r2(rrf, iHDdFHg) = 0.581; r2(imMrFHt, iHDdFHg) = 0.931; r2cv = 0.682 (4)
The graphical representation of best bi-varied MDF QSPR (equation 3) is in figure 3.
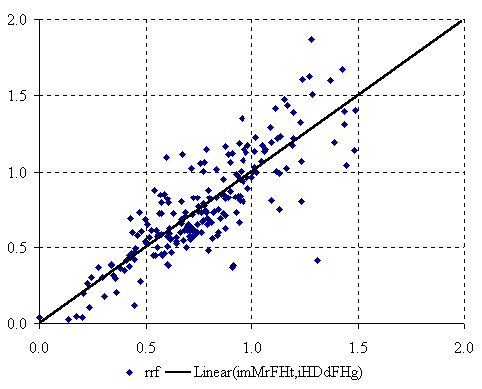
Figure 3. The plot of best bi-varied MDF QSPR
The best found four-varied MDF QSPR is:
· Ŷ=6.055-416.9·imMrFHt+2.314·iHDdFHg+1.829·iMMMjQg-2.51·10-3·iAMrVQg (5)
and the associated statistical results for four-varied QSPR are:
· r = 0.858; r2 = 0.737; s = 0.183; F = 143, p = 5.768·10-58; r2(rrf, imMrFHt) = 0.448; r2(rrf, iHDdFHg) = 0.581; r2(rrf, iMMMjQg) = 0.062; r2(rrf, iAMrVQg) = 0.205; r2(imMrFHt, iHDdFHg) = 0.931; r2(imMrFHt, iMMMjQg) = 0.177; r2(imMrFHt, iAMrVQg) = 0.002; r2(iHDdFHg, iMMMjQg) = 0.111; r2(iHDdFHg, iAMrVQg) = 0.0004; r2(iMMMjQg, iAMrVQg) = 0.025; r2cv = 0.717 (6)
The graphical representation of best found four-varied MDF QSPR (equation 5) is in figure 4.
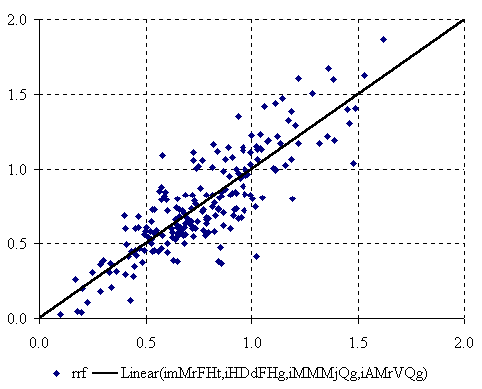
Figure 4. The plot of best found four-varied MDF QSPR
Discussions
The best mono-varied MDF QSPR (equation 1) uses from a total number of 98434 MDF members the iHMdTHg member. The used descriptors take into consideration the geometric distance operator computed using Cartesian coordinates of the PCBs (last character from the descriptor name ‘g’) and the number of directly bonded hydrogen’s (‘H’). The mono-varied MDF QSPR of relative response factor of PCBs is statistical significant giving us a probability of wrong model equal with 2.01·10-44 % (equation (2)). Looking at the statistical results of the QSPR we can say that almost sixty-three percent of variation in PCBs relative response factor can be explain by its linear relations with the MDF member called iHMdTHg. Looking at the leave one out square cross validation score of mono-varied model we can see that this QSPR has good potential of estimation of PCBs relative response factor, having a score equal with 0.619. The mono-varied model shows us that the variation of relative response factor can be assign to geometric conformation and the directly bonded hydrogen’s.
The bi-varied MDF QSPR uses imMrFHt and iHDdFHg molecular structure descriptors (equation 3). The last letters of the descriptors name denote the use of topological distance (t) as well as the geometrical distance (g) in relative response factor estimation of PCBs. The penultimate letters of the members name highlight the importance of the directly bonded hydrogen’s (H) in estimation of the relative response factor of PCBs. Thus, the bi-varied model is a model which takes into consideration the directly bonded hydrogen’s as well as the topological and geometrical distance. The probability of a wrong bi-varied model (equation 4) is equal with 1.556·10-51 %. Sixty-nine percent of the variation of PCBs relative response factor is explainable by its linear relation with imMrFHt and iHDdFHg MDF members. Looking at the statistical result of bi-varied MDF QSPR (equation 4) we can observe that there is a strong linearity between the used MDF members (r2 = 0.931) while the linearity between the relative response factor and each MDF member is a weak one (the r2(Rf, imMrFHt) = 0.448, and respectively r2(Rf, iHDdFHg) = 0.581). The leave one out cross validation score gives us the power of estimation of PCBs relative response factor, which in case of the bi-varied MDF QSPR model is about 0.68.
The four-varied MDF QSPR for relative response factors of PCBs uses the imMrFHt, iHDdFHg, iMMMjQg, and iAMrVQg MDF members. If we look at the MDF members names to the last letter, it can be observed that the four-varied MDF QSPR take into consideration one MDF member which use the topologic distance operator (t) and three descriptors which use the geometrical distance operator (g). If we look at the penultimate letters of MDF members implied in the best found four-varied MDF QSPR it can be observed that two MDF members take into account the number of directly bonded hydrogen’s (H) and the other two the partial change, semi-empirical Extended Hückel model, Single Point approach (Q). The four-varied MDF QSPR is statistically significant giving us a probability of wrong model equal with 5.768·10-56 %.
Almost seventy-four percent of relative response factor variation is explainable by its linear relation with imMrFHt, iHDdFHg, iMMMjQg, and iAMrVQg molecular structure descriptors. The square of correlation coefficient between used MDF members from four-varied MDF QSPR (equation 6) suggest that is no link between using of orthogonal descriptors (Principal and/or Dominant Component Analysis) in four-varied MDF QSPR modeling of relative response factor of PCBs. The four-varied MDF QSPR have a cross validation score equal with 0.717; thus, this model, compared with the mono and bi-varied models, has the greatest estimation ability of PCBs relative response factor.
Inspecting all best or best found QSPRs, we can take into account the presence of iHMdTHg member in mono-varied MDF QSPR, of imMrFHt and iHDdFHg members in bi-varied MDF QSPR and of imMrFHt, iHDdFHg, iMMMjQg, and iAMrVQg members in four-varied MDF QSPR. All of them use the inverse linearization operator (first letter of the names, i) which suggest that the relative response factor (rrf) property is linear on inverse of molecular structure descriptors. The presence of M (maximal fragments) and D (distance-based fragments) on third position of names suggest that rrf is a global molecular property (all atoms from the molecule contribute in approximately same manner to the rrf and rrf is an inter-atomic distance-based property. The “FH” association from member’s names suggests that the hydrogen’s interact with a force-based descriptor to the stationary phase of high resolution gas chromatograph. The “jQ” and “VQ” associations suggest a conservative inverse of distance based interaction of partial atomic charges (j is 1/p∙d and V is p/d) with the stationary phase of high resolution gas chromatograph. The major presence of “g” geometric distance operator in averse of “t” topological distance operator denote that the rrf property is much sensitive to the geometrical shape of the PCBs then molecular topology.
Conclusions
The lower value of squared correlation coefficients of MDF QSPR suggest that the relative response factor property of polychlorinated biphenyls can be explained with at most about 75% using in-vitro molecular structure descriptors, which are a expected result, considering that the elution process are in gas phase, where molecular structure can suffer geometrical conformation changes. The geometrical shape of the molecule is dominant for relative response factor property (three of four descriptors from four-varied MDF model use geometrical distance operator). Atomic partial charge distributions and hydrogen’s play the main role on interactions with the stationary phase of high resolution gas chromatograph.
References