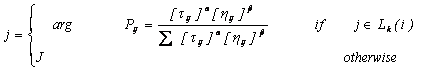Optimal
Placement and Sizing of Capacitor Banks Using Fuzzy-Ant Approach in Electrical
Distribution Systems
Brahim GASBAOUI 1*, Abdelkader
CHAKER2, Abdellah LAOUFI1, Abdessalam ABDERRAHMANI 1 and Boumediène ALLAOUA1
1 Faculty of the sciences and
technology, Department of Technology,
2Laboratory of
SCAMRE, ENST,
E-mail(s): brahim_gasb@yahoo.com; chakeraa@yahoo.fr;
elec_allaoua2bf@yahoo.fr
(*Corresponding
author: Phone: +213 – 762-336-415.)
Abstract
Among optimizations of
reactive power are minimization of total active power losses and control of voltage
in the real-time. This can be achieved by placing the
optimal value of capacitor at proper locations in electrical distribution
systems. The proposed methodology is an intelligent fuzzy-ant approach of
critical buses detection for optimal placement and sizing of capacitor banks in
electrical distribution systems the critical nodal is determiner using fuzzy
controller and the sizing of capacitor banks is obtained based on ant colony
system. Calls up to the ant colony system which are use for complexes
combinatorial problem minimizes the cost function. Voltage constraints are
considered. The proposed fuzzy-ant approach is has been evaluated on a 25 and
30 buses.
Keywords
Critical
Nodal Detection; Capacitor Placement and Sizing; Fuzzy-Ant Approach; Ant Colony
System; Power Flow.
Introduction
Power distribution from
electric power plants to ultimate consumers is accomplished
via the transmission sub transmission, and distribution lines. Studies have
indicated that as much as 13% of total power generated is
consumed as RI2 losses at the distribution level. The RI2
losses can be separated to active and reactive
component of branch current, where the losses produced by reactive current can
be reduced by the installation of shunt capacitors. Capacitors are widely used
in distribution systems to reduce energy and peak demand losses, release the
KVA capacities of distribution apparatus and to maintain a voltage profile
within permissible limits. The objective of optimal capacitor placement problem
is to determine the size, type, and location of capacitor banks to be installed on radial distribution feeders to achieve
positive economic response. The economic benefits obtained from the loss
reduction weighted against capacitors costs while keeping the operational and
power quality constraints within required limits.
Fuzzy logic provides a
remedy for any lack of uncertainty in the data. Furthermore
fuzzy logic has the advantage of including heuristics and representing engineering
judgments into the capacitor allocation optimization process.
The ACS is a
meta-heuristic motivated by the behaviour observed in colonies of real ants for
finding the shortest path from a food source to their nest. Ants can find the
shortest path because they deposit pheromones on paths they visit and they
follow paths with higher pheromone trails. In [2], the ACS was proposed to
solve the travelling salesman problem (TSP) by
generating successively shorter feasible tours using information accumulated in
the form of a pheromone trail deposited on the edges of the TSP graph.
Many of the previous
strategies for capacitor allocation in the literature are also limited for the
application to planning, expansion or operation of distribution systems. Very few
of these capacitor allocation techniques have the flexibility of being
applicable to more than one of the above problems. Hence, this paper presents a
fuzzy-ant approach to determine suitable locations for capacitor placement and
the sizing of the capacitor. This approach has the versatility of being applied to the planning, expansion, and operation
studies of distribution systems. The proposed method was
tested on electrical distribution systems consisting of 25 buses
distribution system.
Mathematical
Formulation
The
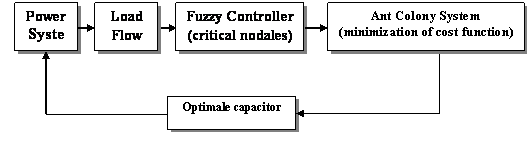
Figure
1. Bloc of intelligent fuzzy-ant approach
The objective function
of placements to reduce the power loss and keep bus voltage within prescribed
limits with minimum cost .The constraint are voltage limits .Following the
above notation, the total annual cost function due to capacitor placement and
power loss is written as [10]:
|
|
(1) |
Constraint of voltage:
|
Vimin ≤ Vi ≤ Vimax i = 2, 3, … N |
(2) |
where: F = Total annual cost
function [$], KPL = Annual cost per unit of power
losses [$/kW], PL = Total active power loss [kW], KCj = Capacitor annual cost [cost/KVar], Bj =
Shunt capacitor size placed at bus j [kVar], N
= Number of buses, Vmin = Minimum
permissible rms voltage, Vmax
= Maximum permissible rms voltage.
Fuzzy Logic
Controller
Fuzzy logic is expressed by
means of the human language. Based on fuzzy logic, a fuzzy controller converts
a linguistic control strategy into an automatic control strategy, and fuzzy
rules are constructed by expert experience or
knowledge database.
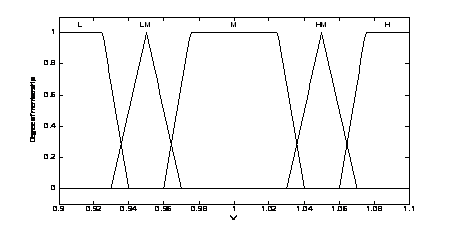
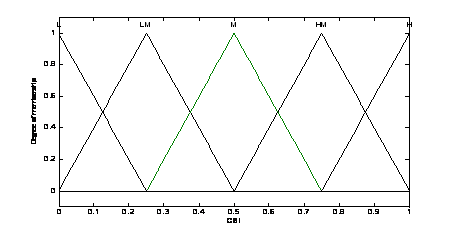
First, set the power loss index
The linguistic variables are defined as {L, LM,
M, HM, H}, where L means low, LM means low
medium, M means medium HM means height medium and H means
height. The membership functions of the fuzzy logic controller are shown in Fig. 3, Fig. 4 and Fig. 5. The fuzzy rules are summarized in Table 2. The surface of fuzzy controller is shown in Fig. 6. The type of fuzzy inference engine is Mamdani. The fuzzy inference mechanism in this study
follows as:
|
|
(4) |
where ![]() is the membership function of
is the membership function of ![]() is
the membership function of V,
is
the membership function of V, ![]() is the
membership function of SCI, j is an index of every membership
function of fuzzy set, m is the number of rules and is the inference result.
Fuzzy output CSI can be calculated by the centre of
gravity defuzzification as:
is the
membership function of SCI, j is an index of every membership
function of fuzzy set, m is the number of rules and is the inference result.
Fuzzy output CSI can be calculated by the centre of
gravity defuzzification as:
|
|
(5) |
where i = the output rule
after inferring.
Fuzzy Based Capacitor Location
Node voltages and power loss indices are the inputs to
fuzzy controller to determine the suitability of a node in the capacitor
placement problem. The suitability of a node is chosen
from the capacitor suitability index (CSI) at each node. The higher
values of CSI are chosen as best locations for capacitor placement [1,
2, 3, 4, 5].
The power loss indices are
calculated as:
|
|
(6) |
where: LR : Loss reduction, LMIN
: Minimum reduction, LMAX : Maximum reduction, N :
Number of bus.
To determine the critical busses the voltage and power
loss index at each node shall be calculated and are
represented in fuzzy membership function. By using these voltages and
|
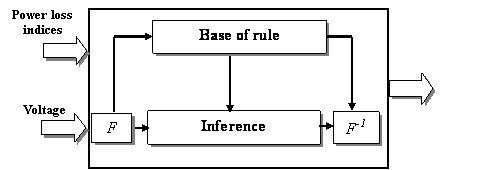
Figure 2. Structure of Fuzzy Controller (where: F = Fuzziffication; F-1
= Defuzziffication)
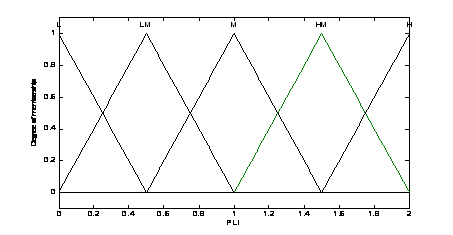
Figure
3. Power loss indices membership
Figure
4. Voltage membership functions
Figure
5. Capacitor suitability index membership function
Table
1. Decision matrix for determining suitable capacitor
|
CSI |
V |
|||||
|
L |
LM |
M |
HM |
H |
||
|
|
L |
L |
L |
L |
LM |
LM |
|
LM |
L |
L |
LM |
LM |
M |
|
|
M |
L |
L |
LM |
M |
HM |
|
|
HM |
L |
LM |
M |
HM |
HM |
|
|
H |
LM |
LM |
M |
HM |
H |
|
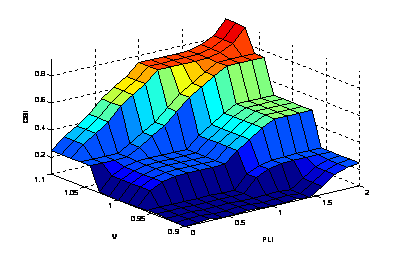
Figure
6. View plot surface of fuzzy controller
Algorithm
for critical busses identification
Following algorithm explain the methodologies to identify
critical busses, witches are more suitable for capacitor placement [6, 10].
Step1: Read line and load data
of power system.
Step2: Calculate power flow
Newton Raphson methods
Step3: Determine total active
power loss.
Step4: By compensation the self –reactive power at each node and
conduct the load flow to determinate the total active power losses in each
case.
Step5: Calculate the power
loss reduction and power flow loss indices.
Step6: The
Step7: The outputs of
Fuzzy controller are deffuzzified. This gives the
ranking of CSI. The nodes having the highest value of CSI are the
most suitable for capacitor placement.
Step8: Stop.
Ant Colony System
(ACS)
Overview
The ACO algorithms form a class of meta-heuristic to
solve NP-hard combinatorial optimization problems. It has been introduced to
solve the travelling salesman problem. The basic idea
is to imitate the behavior of real ants foraging for
food. In fact, the real ants can found the shortest path from a food source to
their nest without visual cue. Indeed, they communicate, in a local and
indirect way, through an aromatic essence called “pheromone”, deposed on the
ground as they move about. Being very sensitive to this substance, an ant
seeking food choose, in a randomly way, the path comprising a strong
concentration of this substance. Thus, as more ants take the same path, more than ants will be attracted by this path. By analogy,
in ACO algorithm, artificial ants build a solution by applying a probabilistic
decision to choose a next destination. The generation of solutions is guided by
pheromone trail and information related on the problem specification. Then, the
ACO can be defined as an extension of traditional construction heuristics which have to adapt the pheromone quantity during
the execution of the algorithm to take, into account, the experiment of
research. We note that, in addition to the real ants characteristics, the
artificial ants are equipped with a memory, are not completely blind, and the
used time is discrete.
The Ant Colony System ACS is a particular approach of
the ACO, proposed by [12-13] to solve the travelling salesman
problem. In the ACS, a set of cooperation agents (ants), initially positioned
at a starting point with a number of destination points, cooperate to find
routes according to some rules. In fact, each ant builds a feasible solution by
applying a probabilistic function based on the pheromone trail and a heuristic
function. While constructing its solution, an ant changes pheromone level of
the selected edge by applying a local updating rule. Once all the ants have
completed their solution, a global updating rule is performed [11-18].
Implementation
of ant colony system based capacitor sizing
To apply the ant colony system (ACS) algorithm to a
combinatorial optimization problem, is reside to represent the problem by a
matrix G = [n, r].
|
|
(4) |
where: n = Number of capacitor size; r = Number of
critical busses
An ant positioned on
node i chooses the capacitor j by
applying the rule given by:
|
|
(5) |
And j is a random variable
selected according to the probability distribution given by:
|
|
(6) |
α and β are parameters
that control the relative weight of the pheromone. A Ci
is the set of available Components or capacitors. While
constructing its solution, an ant also modifies the amount of pheromone on the
visited capacitor by applying the local updating rule: While building a
solution of the problem, ants choose elements by visiting element on the matrix
G, and change their pheromone level by applying the following local
updating rule:
|
|
(7) |
where ρ is a coefficient such that (1-ρ)
represents the evaporation of trail and τ0 represent the
initial trail of pheromone. Once all ants have terminated their tour, the
amount of pheromone on capacitor size is modified an
Ant colony system in (by applying the global updating rule): Once all ants have
built a complete system, pheromone trails are updated. Only the globally best
ant (i.e., the ant which constructed the best solution
from the beginning of the trial) is allowed to deposit pheromone. A quantity of
pheromone Δτij
is deposited on each capacitor size that the best ant has used. Therefore,
the global updating rule is:
|
|
(8) |
where 0 < ρ < 1 is the pheromone decay
parameter representing the evaporation of trail and Δτij
represent the lay of the pheromone in the Capacitor C (i, j). Ants are guided, in building their tours, by
both heuristic information (they prefer to choose "less expansive" element),
and by pheromone information. Naturally, an element with a high amount of
pheromone is a very desirable choice. The pheromone updating rules are designed
so that they tend to give more pheromone to element which
should be visited by ants.
Ant
colony algorithm for size capacitor computing
The Ant colony system based capacitor sizing algorithm
is given below:
Step1: Initializing pheromone
an visibility each element of matrix G,
For i = 1:n
For j= 1:r
τij
= τ0
ηij = 1/F
End For
End For
Step2: In this phase each ant builds their tours. The tour of ant is stored
in tabu list,
While k ≤ p (stopping criterion is
no wet met)
For l = i:m
For s = l:r
§
Choose the next element
of matrix G according to formula (5) and formula (6),
§
Stored in tabu list,
§
For each chosen element local updating
occurs and pheromone is updated using formula (7),
End For
§
Evaluate the fitness
for each combination according to the objective function (including penalty
function). The fitness function includes the total cost investment F and the penalty functions .the penalty function used
in implantation is quadratic .It act as a soft constraint .The constraint
includes the bus voltage at each bus:
- Find
the minimum (F best) among m1 cost
functions,
End For
Step 3: In this phase global updating occurs and
pheromone is updated,
- Update
elements of matrix G belonging to F best using
formula. (8) and
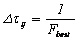 .
.
End While.
where: m = Number of ant; p = Number
of maximum cycle.
Results and
Discussion
The proposed method is illustrated with a system,
consisting of 25 bus. The location
for placement of capacitors is determined by fuzzy controller and the
capacitor sizes are evaluated using ant colony system.
KPL was selected to be 168 $/kW, and voltage limits
on the rms voltage were selected as Vmin = 0.95 pu and Vmax
= 1.10 pu.
Fuzzy-Ant is applied for 25 buses
electrical distribution systems the results of approach given above are shows
at table 2.fu Ant colony system parameter setting are show in table 3.in Table
we show that the active power losses are decrease for e 29.8913 at 23.2082 MW,
decreasing 22.358% and the minimal voltage are improved to 0.9241 at 0.9639 pu.
Table
2. Results of Fuzzy-Ant approach for 25 buses
|
N° of critical buses |
Value of capacitor [MVARS] |
Active power loss [MW] |
Minimal voltage [PU] |
||
|
|
Before placement of optimal capacitor |
After placement of optimal capacitor |
Before placement of optimal capacitor |
Before placement of optimal capacitor |
|
|
7 |
9.00 |
29.8913 |
23.2082 |
0.9241 |
0.9636 |
|
8 |
5.00 |
||||
|
10 |
8.00 |
||||
|
11 |
5.00 |
||||
|
Optimal annual cost |
1262226 $ |
||||
The different voltages of 25 bus electrical network
given before ant colony system are illustrated in Fig.
7.
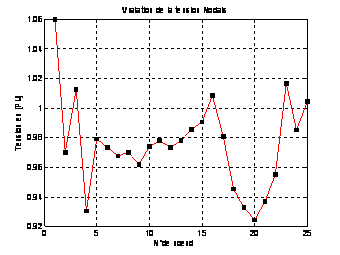
Figure
7. Voltage before optimization
The different voltages of 25 bus electrical network
given after ant colony system are illustrated in Fig.
8. The 30 buses electrical network topology is presented
in Fig. 9.
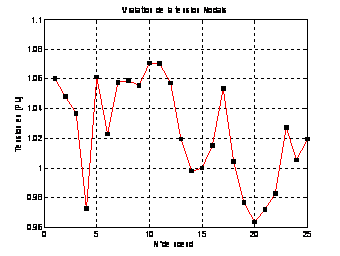
Figure
8. Voltage before optimization
Fuzzy-Ant is applied for 30
buses electrical distribution systems the results of approach given above are
shows at table 3. Fu Ant colony system parameters setting are show in table 4.
In Table we show that the active power losses are
decrease for 9.457 at 6.645MW, decreasing 29.67 % and the minimal voltage are
improved to 0.959at 0.968 pu.


Figure
9. The 30 buses electrical network
Table
3. Results of Fuzzy-Ant approach for 30 buses
|
N° of critical buses |
Value of capacitor [MVARS] |
Active power loss [MW] |
Minimal voltage [PU] |
||
|
|
Before placement of optimal capacitor |
After placement of optimal capacitor |
Before placement of optimal capacitor |
Before placement of optimal capacitor |
|
|
7 |
4.00 |
9.457 |
6.645 |
0.959 |
0.968 |
|
12 |
2.00 |
||||
|
19 |
5.00 |
||||
|
26 |
2.00 |
||||
|
27 |
5.00 |
||||
|
Optimal annual cost |
762226 $ |
||||
Table
4. Ant colony systems parameters
|
|
Ant colony system parameter setting |
Value |
|
|
Alpha parameters that control the relative weight of the pheromone. |
1 |
|
|
Beta parameters that control the relative weight of the pheromone. |
5 |
|
|
Initial pheromone trails. |
0.1 |
|
|
Parameter of evaporation. |
0.5 |
|
|
Number of maximum cycle. |
100 |
|
|
Number of |
10 |
|
|
Heuristic information. |
|
Conclusions
This paper introduces an
intelligent Fuzzy-Ant approach method to determinate a critical busses by fuzzy
controller and ant colony system (ACS) for minimization a total cost investment
for capacitor this combination reduce active power losses and improve the bus
voltage .The main advantage of this approach is robustness of ant colony
systems, over modern heuristic is flexibility, robustness of the complex
combination problem, sure and fast convergence. As a study case the 25 buses
system and 30 buses, the simulation results show that for medium-scale system
an ant colony optimization method can give a best
result.
Ant colony system parameter alpha, beta and visibility
play an important role in the performance of ant colony system and some
permutations and combinations of these parameters are to be
tested to get the best performance.
References
1.
Baran M.E., Wu F.F., Optimal capacitor
placement on radial distribution systems, IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, 1989,
4, p.725-734.
2.
Baran M.E., Wu F.F., Optimal sizing of
capacitors placed on radial distribution systems, IEEE Trans. Power
Delivery, 1989, 4, p.735-743.
3.
Ponnavaiko M., Prakasa
R.K.S., Optimal choice of fixed and switched capacitors on radial
distribution feeders by the method of local variations, IEEE Trans. Power
Apparatus and Systems, 1983, vol. 102, p.1607-1615.
4.
Grainger J.J., Lee
S.H., Optimum size and location of shunt capacitors for reduction of losses
on distribution feeders, IEEE Trans. Power Apparatus and Systems, 1981,
100, p.1105-1118.
5.
Das D., Novel method for solving
radial distribution networks, IEE Proc. C, 1994, 141, p. 291-298.
6.
Bouri S., Zeblah
A., Ghoraf A., Hadjeri S., Hamdaoui H., Ant colony optimization to shunt capacitor
allocation in radial distribution systems, Acta Electrotechnica et Informatica,
2005, 4(5), [online], Available at:
http://www.aei.tuke.sk/pdf/2005-04/Bour.pdf.
7.
Prasad P.V., Sivana S., Sreenivasulu N., A
fuzzy-genetic algorithm for optimal capacitor in radial distribution systems,
ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 2007, 2(3), p. 28-32.
8.
Parpinelli R., Lopez H.S., Freita
A.A., Data mining with ant colony optimization algorithm, IEEE
Transaction on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(4), p. 321-332.
9.
Semet Y., Lutton
E., Collet P., Ant Colony Optimization for
e-learning Oberserving the emergence of pedagogic
suggestions.
In IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium 2003.
10.
Gabriel Estrada Soria
Morelia, Mich., Febrero, Metodología Técnico-económica de Localización de
Capacitares en Sistemas de Distribución para la Reducción de Pérdidas
Eléctricas, thesis 2003.
11. Taillard E., Ant systems, Handbook of
Applied Optimization, P. PARDALOS, M.G.C RESENDE.
12.
Dorigo M., Gambardella M., Ant Colony
System: A Cooperative Learning Approach to the Travelling Salesman Problem,
IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 1997, 1, p. 53-66.
13.
Dorigo M., Gambardella L. M., Ant
colony system: a cooperative learning approach to the travelling salesman problem, IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary
Computation, 1997, 1(1), p. 53-66.
14.
Dorigo M., Maniezzo
V., Colorni A., Ant system: optimization by a
colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics-Part B: Cybernetics, 1996, 26(1), p. 29-41.
15.
Dorigo M., Gambardella L. M., Middendorf M., Stutzle T., Guest
editorial special section on ant colony optimization. IEEE Transactions on
Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(4), p. 317-319.
16. Gambardella L.M., Dorigo M., Ant-Q: a reinforcement learning approach to
the traveling salesman problem, Proceedings of
ML-95, Twelfth International Conference on Machine Learning, A. Prieditis and S. Russell (Eds.), Morgan Kaufmann, pp.
252-260, 1995.
17.
Gambardella L.M., Dorigo M., Solving Symmetric and Asymmetric
18.
Zhang J., Hu X., Tan X., Zhong J. H., Huang
Q., Implementation of an Ant Colony Optimization technique for job shop
scheduling problem, Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and
Control, 2006, 28, p. 93-108.